Microbial identification (MALDI-TOF)
Code: 61030, 61033
Type: Control de qualitat de medicaments de teràpia avançada
Technical information
Utility
Identifying a microorganism at the genus and species level. The microorganism can come from environmental culture or from a culture of blood components, milk, tissues, cell therapy, advanced therapy, etc.
Method
There are several methods to identify a microorganism, which can be complementary:
-
Studying phenotypic characteristics:
-
Microscopic morphology (staining and observation under the microscope)
-
Metabolism (biochemical tests)
-
Antigenic composition (serological studies)
-
Biomolecular composition (MALDI-TOF)
-
-
Studying genotypic characteristics:
-
Genome (Sequencing, PCR)
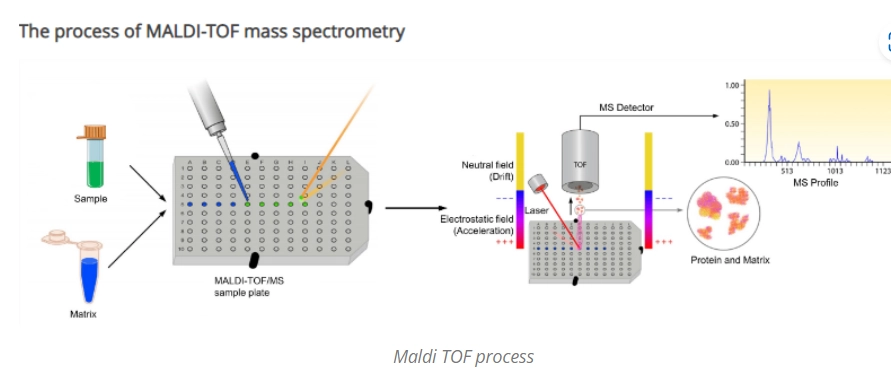
MALDI-TOF: From the English acronym MALDI (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization) and TOF (Time-Of-Flight). MALDI-TOF is a gentle ionization technique that hits large molecules with laser energy and releases ionized fragments. The measurement principle is shown in illustrations 1 and 2.
The sample to be analysed is mixed or coated with an organic compound containing an absorbent solution called matrix. The matrix acts as an energy absorber for laser irradiation. The matrix compounds with the analyte are deposited on a plate made of a conductive metal. Then, with a laser beam, the sample is ionized. The matrix molecules desorb and ionize energetically in the presence of a laser beam, generating analyte molecules in the gas phase. The ions are accelerated and separated based on their mass and charge ratio. Small ion molecules accelerate more quickly than large ion molecules. These ions are then detected and measured using the time-of-flight analyser (TOF).

The basic principle of the TOF analyser is to determine the time it takes for the ion to travel the length of the flight tube. Smaller, lighter ions travel faster to the detector than larger, heavier ones. Detection of ions generates a specific spectrum, which is compared with the database to determine the identity of the microorganism.
Diagnostic Algorithm
If microbial growth is detected, the microorganism is identified by MALDI-TOF. Therefore, this test is added when the culture is positive.
Results
The expected result is identification at the genus and species level. In some cases, only identification at the genus level can be obtained. If the microorganism is not in the database, other methods must be used for identification.
Precautions
A pure culture of the microorganism is required for identification.
Response Time
-
1-2 days
Specimen information
Sample: Product or environmental cultivation
Tubes: According to the product (see the records of the tests for each type of cultivation)
Stability: Transport as soon as possible to the laboratory.
Transport instructions: Room temperature.
Reason for rejection: Unidentified sample, illegible label, etc.
Administrative information
BST Code: Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for aerobes (61033) or Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for anaerobes (61030)
Previous BST Code: Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for aerobes (7575) or Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for anaerobes (7572)
Test Description: Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for aerobes, Identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing for anaerobes
Synonyms: Microbial identification, bacterial identification, fungal identification
Section: Microbiology
BST Rates: Check the updated rates here.
Profiles
Not applicable
References
-
Guide to the quality and safety of tissues and cells for human application. 5th edition EDQM, 2022
-
Farmacopea Europea 11ena edició, 2023