Environmental microbiological control of gloves
Code: 60003, 60007
Type: Control de qualitat de medicaments de teràpia avançada
Technical information
Utility
Clean rooms or white rooms are specially designed to ensure low contamination levels and have environmental parameters strictly controlled by regulations. Environmental microbiological controls allow knowing the microbiological conditions of the facilities, equipment, and operators, in order to ensure compliance with the regulations.
The most common origin of microorganisms found in a facility is:
-
The personnel entering the facility.
-
The material entering the facility.
-
The air filtration system (HEPA filters for clean rooms).
The elements that can be contaminated with microorganisms and pose a risk are:
-
Air: Environmental air or laminar flow hoods
-
Surfaces: Floors, walls, tables, handles, etc.
-
Equipment: Incubators, laminar flow hoods, centrifuges, refrigerators, microscopes, balances, etc.
-
Apparel: Gloves, operator's clothing.
The definition of the points and frequencies of environmental control is based on an environmental risk analysis done before the start of activities at a facility, which reviews the rooms, equipment, materials, workflows, the number of people working there, and other factors.
Method
The plates used for environmental microbiological control are shown in Table 1. The plates contain the appropriate culture media for the growth of bacteria and fungi. They also include agents that neutralize the possible presence of disinfectants to prevent them from interfering with the growth of microorganisms.
Before using a batch of plates, a growth promotion test is performed to verify if that batch of plates allows the growth of microorganisms.
|
Medium |
Technique |
Element to control |
Microorganisms |
|
TSA contact with neutralizing agents 55 mm plate |
Contact |
Surfaces |
Bacteria |
|
SDA contact with neutralizing agents 55 mm plate |
Fungi |
||
|
TSA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Volumetric air |
Air |
Bacteria |
|
SDA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Fungi |
||
|
TSA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Sedimentation air |
Air |
Bacteria |
|
SDA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Fungi |
||
|
TSA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Fingerprints |
Gloves |
Bacteria |
|
SDA with neutralizing agents 90 mm plate |
Fungi |
Table 1. TSA: Tryptone Soya Agar medium. SDA: Sabouraud Dextrose Agar medium
The most appropriate environmental microbiological control techniques for the points to be monitored are shown in Table 2:
|
Element |
Technique |
|
Air |
Volumetric or sedimentation air sampling |
|
Surfaces |
Contact |
|
Operator |
Glove fingerprints |
Table 2: Techniques used for sampling different elements.
The sampling technique for gloves is done by touching the fingers on the plate, as shown in Figure 1. It is done twice, once with a plate for fungi and once with a plate for bacteria. A fingerprint of the fingers should be made, without pressing the nails, with constant pressure.
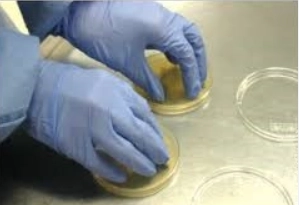
The plates must be sent to the Microbiology Laboratory as soon as possible after sampling. They are received and incubated:
-
TSA plates are incubated at 32.5oC (30oC - 35oC) for 3-5 days for bacteria
-
SDA plates are incubated at 22.5oC (20oC - 25oC) for 5-7 days for fungi.
A negative internal control is also included to ensure that the plates are not contaminated in the Microbiology Laboratory.
Specimen information
Sample: Gloves (contact)
Tubes: 90 mm TSA plate for bacteria and SDA for fungi
Stability: Immediate transport to the laboratory. If not possible, store at room temperature for a maximum of 4 hours.
Transport instructions: Room temperature.
Reason for rejection: Plate not closed properly, unidentified, etc.
Administrative information
Old BST code: 7547 (bacteria) and 7554 (fungi)
Test description: Glove bacteria control, Glove fungus control
Synonyms: Glove CMA, Glove microbiological control
Section: Microbiology
BST rate: Check the updated rates here.
Profiles
Not applicable
References
-
Guide to the quality and safety of tissues and cells for human application. 5th edition EDQM, 2022
-
Farmacopea Europea 11ena edició, 2023
-
ISO 171330-1:2008 Calidad ambiental en interiores. Parte 1: Diagnóstico de calidad ambiental interior.
-
ISO 171330-2:2014 Calidad ambiental en interiores. Parte 2: Procedimientos de inspección de calidad ambiental interior.
-
ISO 171330-3:2014 Calidad ambiental en interiores. Parte 3: Sistema de gestión de los ambientes interiores.
-
ISO 171340:2020 Validación y cualificación de salas de ambiente controlado en hospitals
-
Norma EN ISO 14644-1. Clasificación de sala limpias.
-
Estándares en hemoteràpia CAT
-
FACT-JACIE International Standards for Cellular Therapy Product Collection, Processing, and Administration.
-
NETCORD-FACT International Standards for Cord Blood Collection, Banking, and Release for Administration.
-
NCF: Guía de Normas de Correcta Fabricación de Medicamentos de Uso Humano y Veterinario. Anexo 1
-
NCF Parte IV: Directrices sobre normas de correcta fabricación específicas para Medicamentos de Terapia Avanzada.
-
GpG. Directrices de Buenas Prácticas - Guía para la preparación, uso y control de calidad de los componentes sanguíneos.
-
Real Decreto-ley 9/2014, de 4 de julio, por el que se establecen las normas de calidad y seguridad para la donación, la obtención, la evaluación, el procesamiento, la preservación, el almacenamiento y la distribución de células y tejidos humanos y se aprueban las normas de coordinación y funcionamiento para su uso en humanos.