Technical information
Utility
All human milk donations received at the Milk Bank of the Blood and Tissue Bank undergo a quality control process after being pasteurised, as indicated in the Guide for the Quality and Safety of Tissues and Cells for Human Application 5th edition 2022 and the recommendations of the EMBA (European Milk Bank Association). According to these recommendations, the milk must be microbiologically tested after pasteurisation, discarding batches that do not meet the established requirements. The purpose of this control is to ensure the safety of the milk and prevent the possibility of infections in the infants receiving it.
Method
The European Pharmacopoeia describes in section 2.6.1 the methods to be used to determine sterility. The suitable method for milk is direct inoculation in a liquid medium. However, it is important to note that milk causes turbidity in the liquid medium, making visual reading impossible. Therefore, the microbiological control of post-pasteurised milk is carried out using the direct inoculation method in liquid medium, followed by streaking on agar plate using the following culture media:
-
Trypticase Soy Agar (TSA)
-
Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB)
Furthermore, since the Milk Bank, in case of detecting a contaminated batch, needs to know the quantity of the contaminating microorganism, sections 2.6.12 and 2.6.13 of the Pharmacopoeia are also applied, and the appropriate method is plate count.
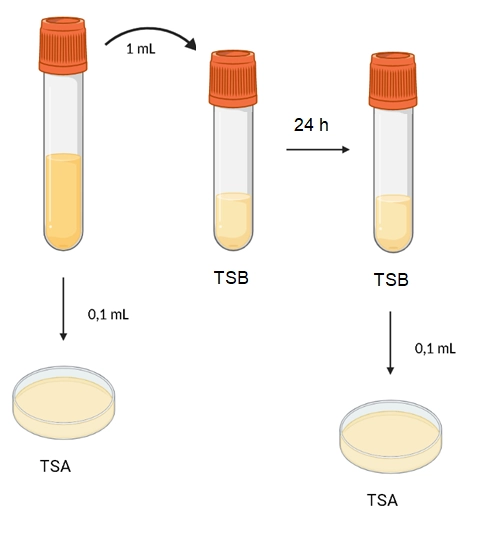
Considering these requirements, the protocol described below has been designed and can be seen in Illustration 1.
Within a laminar flow cabinet and using aseptic technique, with an automatic pipette and sterile tips, 0.1 mL of milk is taken and deposited on the plate. Using a sterile Digralsky loop, the sample is spread and the plate is allowed to dry. With an automatic pipette and a sterile pipette tip, 1 mL of milk is taken and deposited in the TSB liquid medium tube. After 24 hours of incubation, with an automatic pipette and a sterile pipette tip, a 0.1 mL sample of the TSB medium inoculated with milk is taken and deposited on a TSA plate. Using a sterile Digralsky loop, the sample is spread and the plate is allowed to dry. The plates are incubated at 36°C +/- 1°C and read at 24 hours. The colonies are counted, and the concentration of the microorganism in the milk is calculated.
Positive and negative controls are included in each work series.
This method has been validated by the Blood and Tissue Bank, and the validation code is V-LMB-004-
Diagnostic Algorithm
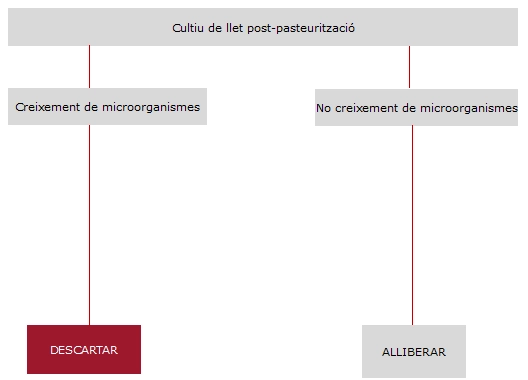
Described in Illustration 2.
Results
Taking into account all the recommendations and in order to ensure the maximum product safety, the Milk Bank applies the following criteria for accepting post-pasteurised milk: any microbial growth is a reason for rejection.
Precautions
Not applicable
Response Time
-
48-72 hours
Specimen information
Sample: Human milk
Tubes: 1 sterile tube
Stability: Frozen: 3 months. Refrigerated: 24 hours.
Transport instructions: Refrigerated.
Reasons for rejection: Container not properly closed, sample not identified, etc.
Administrative information
BST Code: 63801
Old BST Code: 7003
Test Description: Post-pasteurization milk culture
Synonyms: Not applicable
Section: Microbiology
BST Rate: Check the updated rates here.
Profiles
Not applicable
References
-
Guide to the quality and safety of tissues and cells for human application. 5th edition EDQM, 2022
-
Recommendations for the Establishment and Operation of Human Milk Banks in Europe: A Consensus Statement From the European Milk Bank Association (EMBA). Front Pediatr. 2019; 7: 53. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00053
-
Farmacopea Europea 11ena edició, 2023